About Us
What is CelestAI?
CelestAI is an artificial intelligence–driven exoplanet classification system designed to eliminate one of modern astronomy's biggest bottlenecks: the slow, manual, and mission-specific process of distinguishing real exoplanets from false signals. CelestAI automatically classifies detected signals into three scientifically meaningful categories — Confirmed Planet, Planet Candidate, and False Positive — using a unified, multi-mission machine learning framework.
Design & How It Works
CelestAI is built on a merged, cross-mission dataset combining Kepler Objects of Interest (KOI), TESS Objects of Interest (TOI), and K2 mission catalogs. While most existing tools are mission-specific, CelestAI intentionally merges heterogeneous surveys into a single learning space, enabling generalizable predictions across different telescopes and observing strategies.
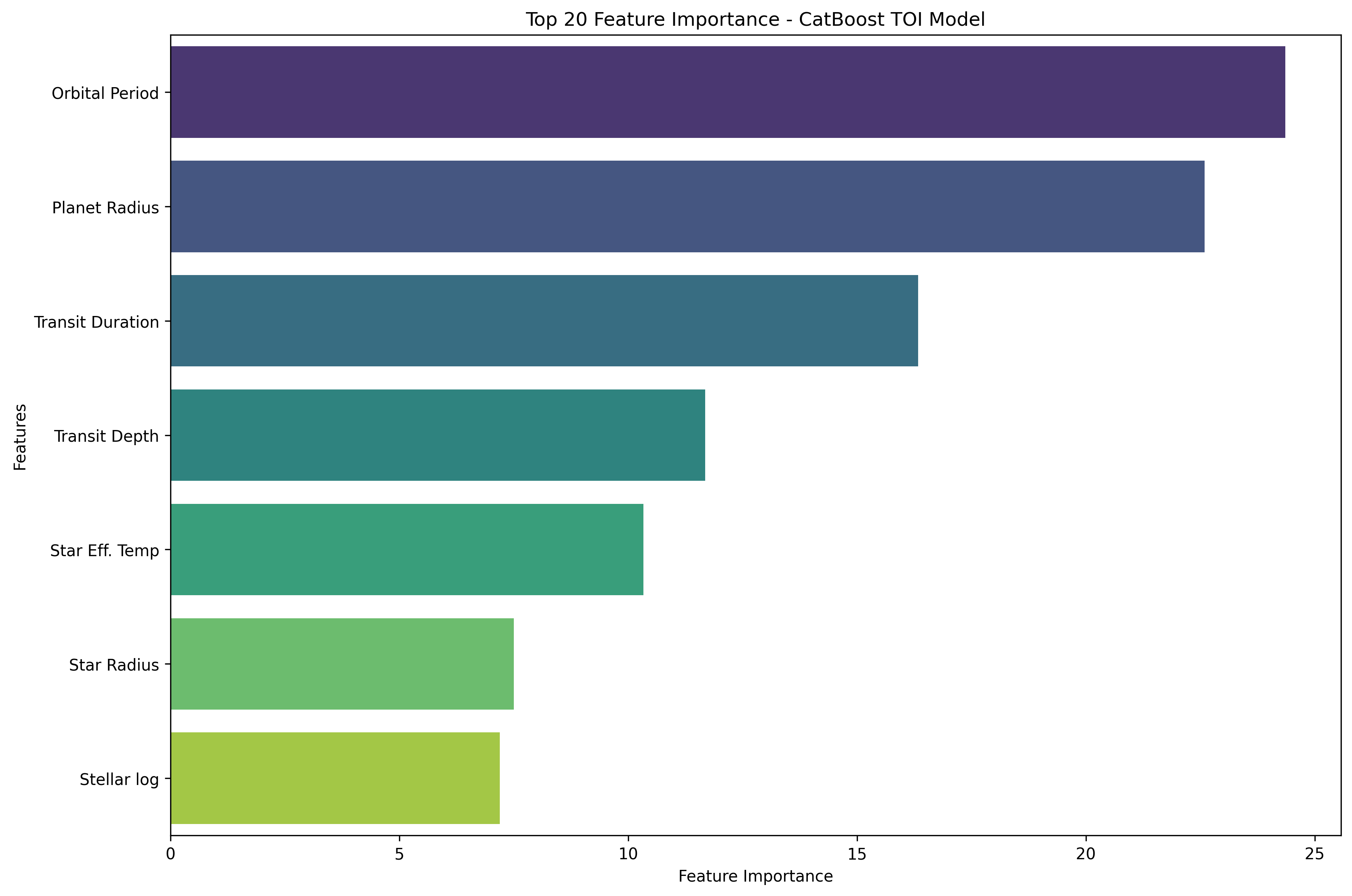
From 7 core astrophysical parameters (e.g., orbital period, transit depth, stellar temperature), we engineered 25+ derived features grounded in physical meaning, such as signal strength metrics, stellar classification encodings, orbital–stellar ratios, and habitability indicators. This feature engineering step is central to CelestAI's performance and interpretability.
The processed data is fed into advanced gradient-boosting models — primarily CatBoost and XGBoost — chosen for their ability to handle non-linear relationships, class imbalance, and noisy real-world scientific data.
Dataset Overview
Our unified dataset combines data from Kepler, TESS, and K2 missions, providing a comprehensive foundation for exoplanet classification:
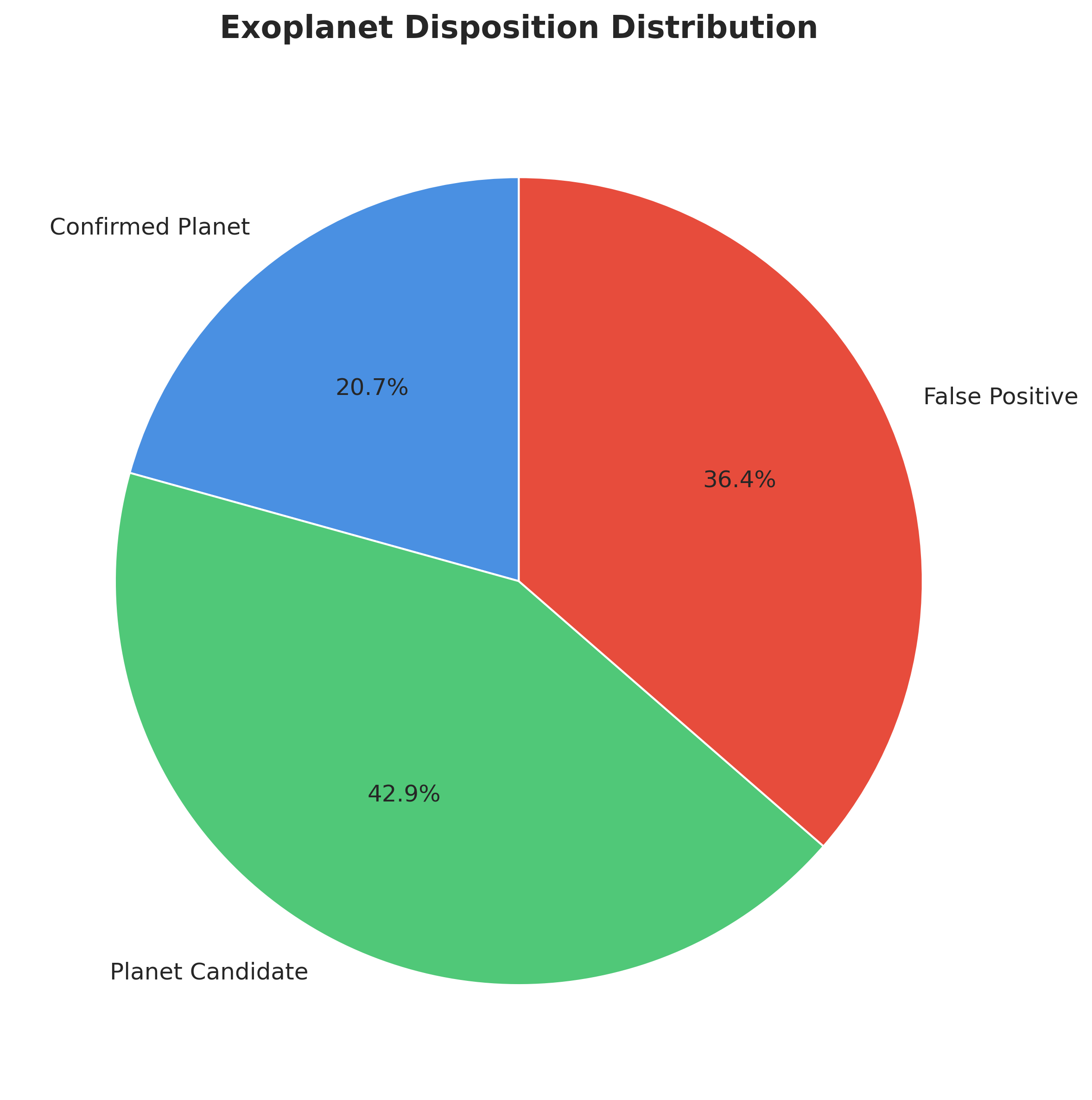
Model Performance
CelestAI achieves state-of-the-art performance through advanced machine learning models. Key metrics and visualizations:
Binary Classification (CatBoost)
Multiclass Classification (XGBoost)
ROC Curve
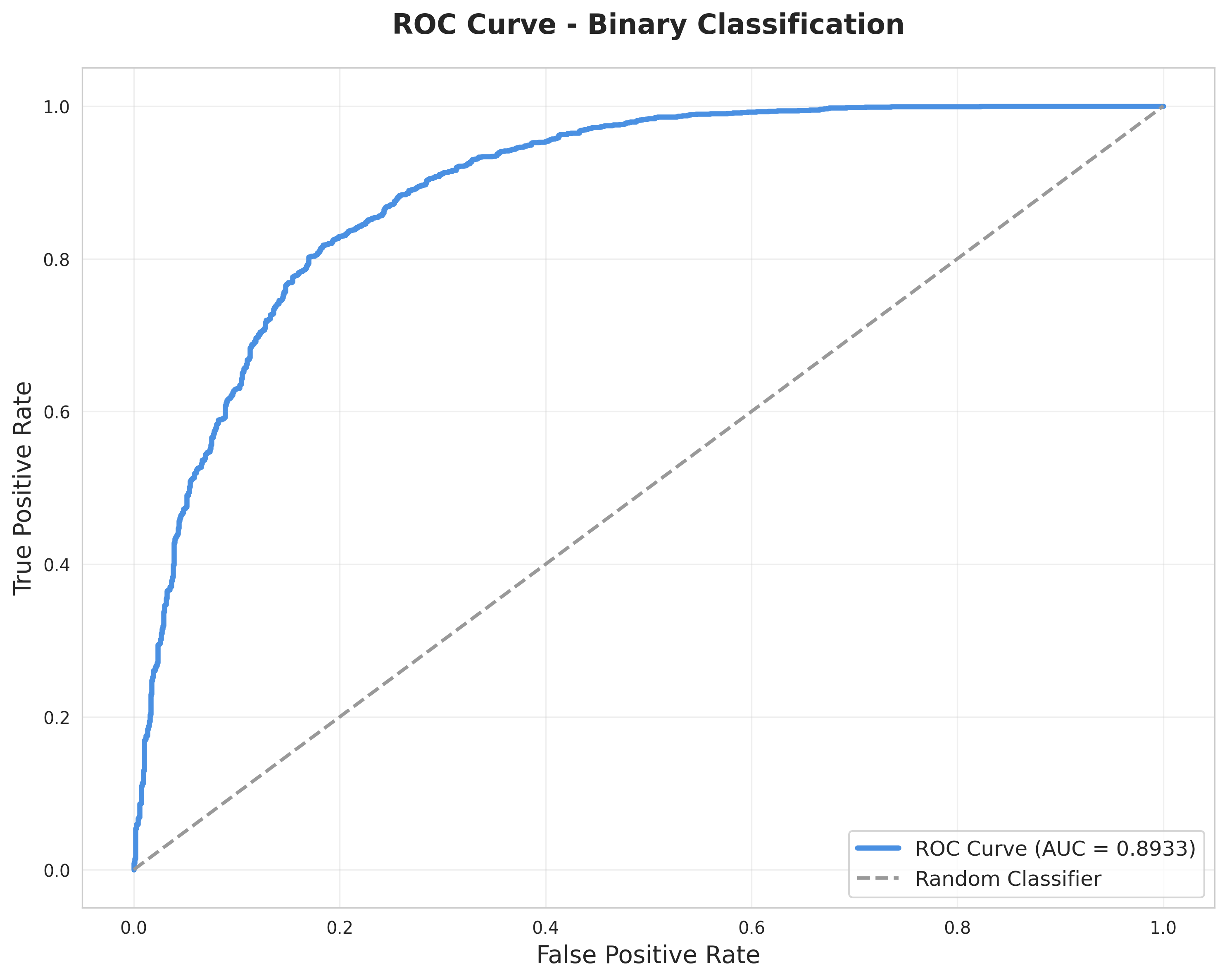
AUC: 0.9276 - Exceptional binary classification performance
Performance Comparison
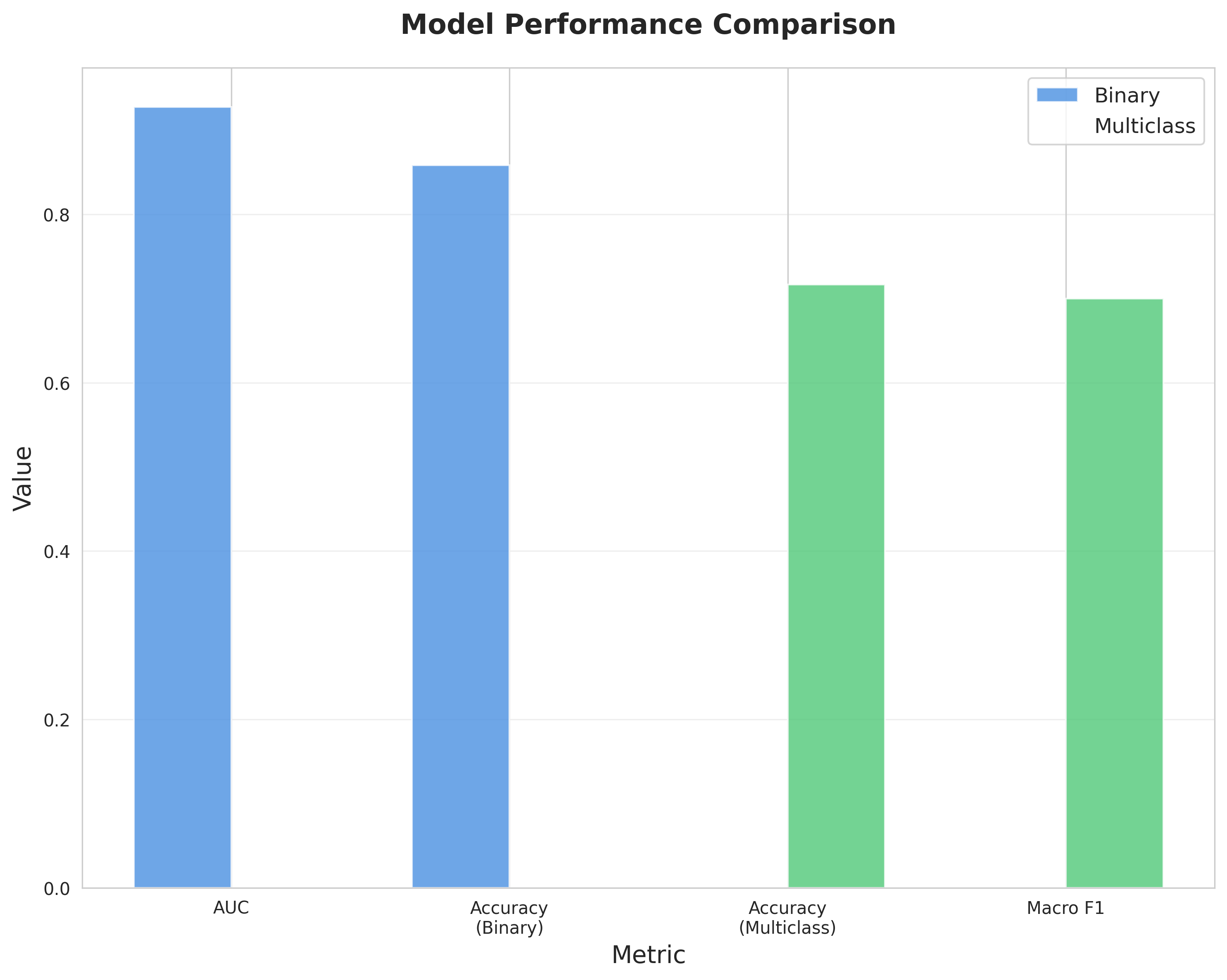
Binary: 85.82% Accuracy | Multiclass: 71.64% Accuracy
Binary Confusion Matrix
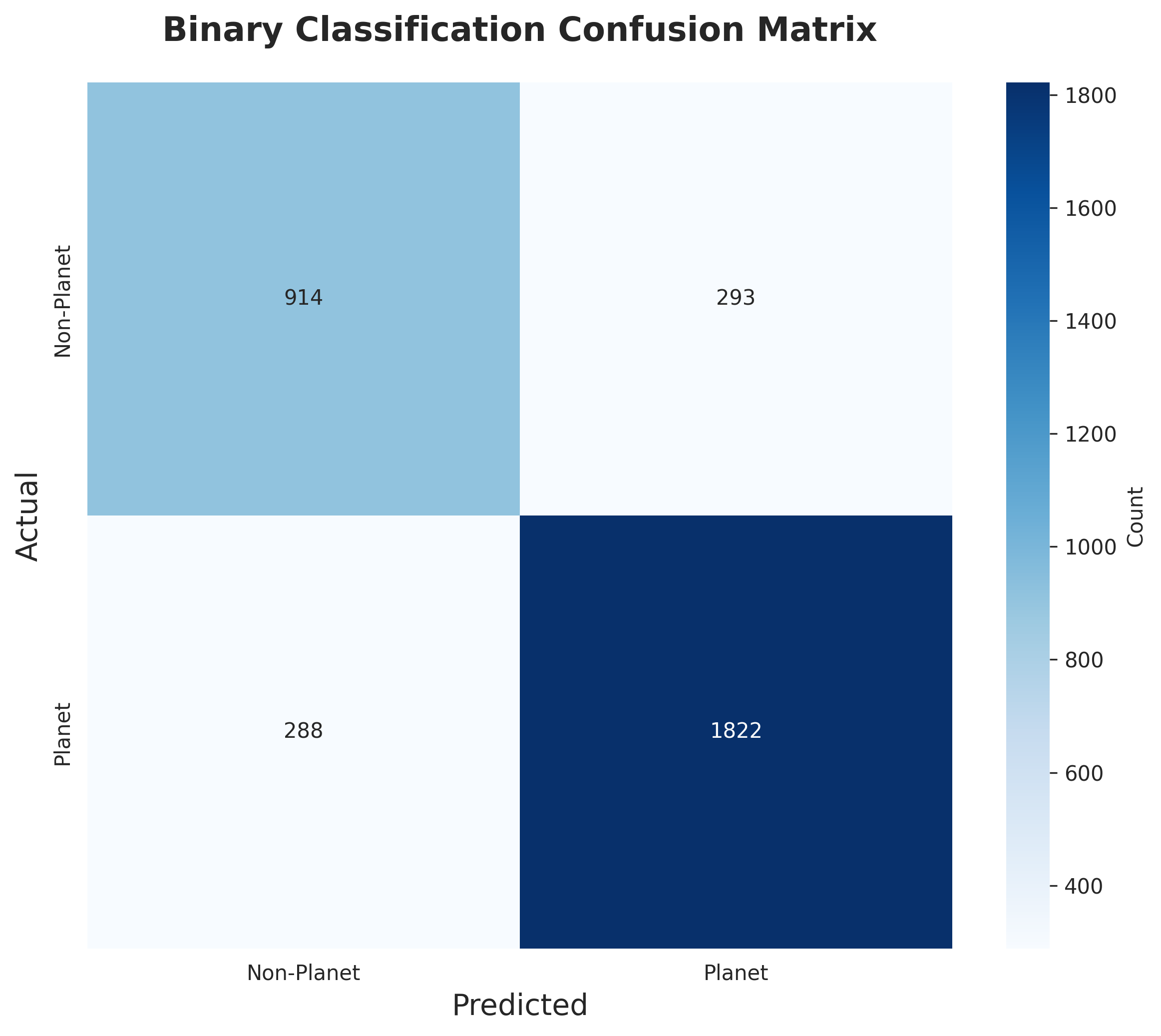
High precision (0.90) and recall (0.88) for planetary signals
Multiclass Confusion Matrix
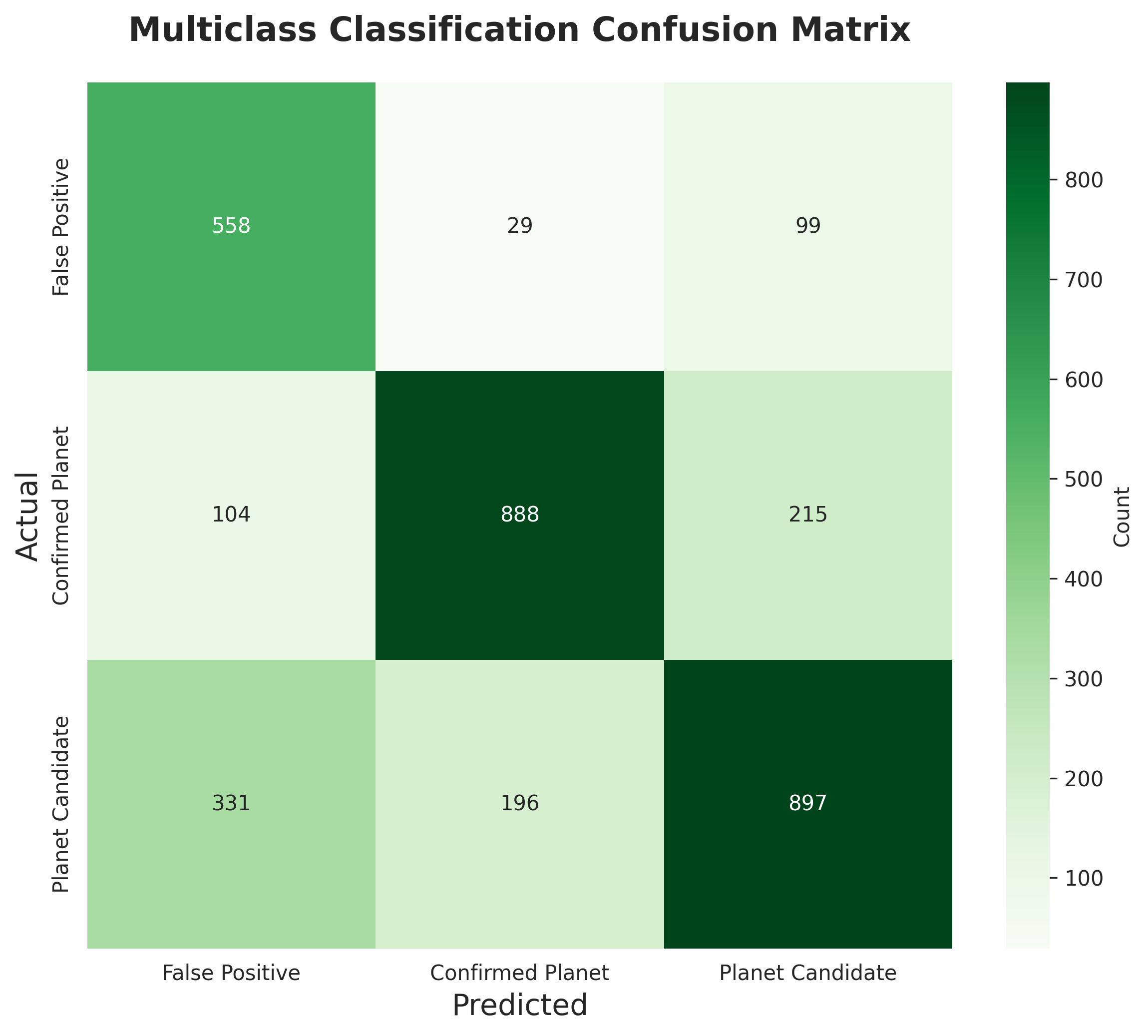
Effective classification across three categories
Binary Feature Importance

Multiclass Feature Importance
What Is New or Proprietary
CelestAI's innovation lies not in "using AI," but in how it applies AI to astrophysics:
Cross-Mission Intelligence
CelestAI is among the first student-built systems to unify Kepler, TESS, and K2 into a single predictive framework, eliminating fragmentation between surveys.
Physics-Aware Feature Engineering
Instead of relying on raw parameters, CelestAI encodes astrophysical relationships (e.g., depth–duration ratios, equilibrium temperature estimates), improving both accuracy and scientific trust.
Explainable AI for Astronomy
Feature importance analysis allows users to understand why a signal is classified a certain way — a critical requirement in scientific research, where black-box models are often rejected.
Retrainable, Deployable Architecture
The API-based design transforms CelestAI from a static model into a reusable scientific tool that can evolve with new mission data.
Needs Addressed & Pain Points Solved
While advanced exoplanet classification pipelines already exist within organizations like NASA, they are not publicly accessible. These systems are typically restricted to internal research teams, leaving small research groups, students, amateur astronomers, and citizen scientists without access to the same analytical power. As a result, high-quality astronomical data is publicly available, but the tools required to meaningfully analyze it are not.
This creates a critical gap: data democratization without tool democratization.
CelestAI directly addresses this imbalance by transforming capabilities that are traditionally confined to large institutions into a public, deployable, and user-friendly platform.
Access Inequality in Scientific Research
Non-institutional researchers and students are effectively excluded from exoplanet classification due to the lack of accessible AI-based tools. CelestAI removes this barrier by providing open, real-time classification, visualization, and retraining capabilities through a web interface and API.
Manual and Time-Intensive Screening
Even within professional research environments, early-stage filtering of false positives consumes a disproportionate amount of expert time. CelestAI automates this process, allowing both professionals and non-professionals to focus on interpretation and discovery rather than repetitive classification.
Fragmentation Across Missions
Existing tools are often mission-specific and incompatible with each other. CelestAI unifies Kepler, TESS, and K2 data into a single framework, enabling consistent analysis across surveys without requiring mission-specific expertise.
Impact
For Researchers
CelestAI can reduce early-stage candidate filtering time by weeks per dataset, allowing astronomers to focus on validation and discovery rather than manual triage.
For Education & Public Engagement
Students and enthusiasts gain access to real NASA data through an intuitive, visual, and scientifically accurate interface — transforming abstract astronomy into hands-on exploration.
For Humanity
By accelerating the discovery of exoplanets, especially potentially habitable worlds, CelestAI contributes to one of humanity's most fundamental questions: Are we alone? Faster discovery directly translates to faster scientific progress.
Protection & Competitive Defensibility
CelestAI's value is defensible through multiple mechanisms:
- Trade Secrets: Proprietary feature engineering pipeline and preprocessing logic
- Copyright: Source code, trained models, and interface design
- Data Moat: Curated, cleaned, and engineered multi-mission dataset
- First-Mover Advantage: Few accessible tools currently unify missions while remaining explainable and retrainable
CelestAI is not just a model — it is an extensible, mission-agnostic exoplanet discovery platform. It bridges artificial intelligence and astrophysics in a way that is scientifically rigorous, practically deployable, and accessible to the next generation of explorers.